Six ways the rail sector can benefit from geospatial analytics (Guest blog by Orbital Insight)
The UK rail industry is one of the most efficient in Europe, with over 980 million passengers and 78m tonnes of freight lifted each year. Passenger numbers are expected to reach 2 billion by 2025, and freight volumes are expected to grow by 20%. This growth will be driven by continued investment in infrastructure, rolling stock, and the continued switch from road to rail for passengers and freight.
With 31,218 km of track spanning the UK, the sheer scale of the track is one of the biggest challenges in the rail network. How do you make data-driven network-wide optimisations? Geospatial data can help.
What is geospatial data, and how can it support growth in the rail industry?
Geospatial data is any data point that has a physical location; a few examples include satellite imagery, mobile phone location data, connected vehicles and maritime ships. The ongoing proliferation of rich geospatial data sources, image processing, machine learning algorithms, and inexpensive cloud computing is giving decision-makers unprecedented insights into what’s happening on and to the earth and can be used to model networks, identify changes, detect movement patterns and monitor activity levels at scale.
Here are some ways geospatial data can support growth in the rail industry:
-
Network Analysis: The UK rail network is large, fragmented and complex. Geospatial data can be used to monitor real-world movement patterns at scale.
-
Railcar Counting: Detects changes in the number of railcars, which could indicate delays, changes in export volumes or activity at specific locations.
-
Route Planning: Geolocation data can be used to help plan new routes. This data can help identify things like land types, land owner registry and where to route new lines.
-
Demand Planning: To locate key areas of highest passenger and freight demand so that enhancements can be made and services can be improved to maximise utilisation.
-
Safety and Security: It can also be used to help identify potential hazards and even help with things like security planning.
-
Marketing: Geolocation data can also be used to help with marketing in the rail industry. This data can help identify potential customers and improve targeting.
Geospatial Data in Practice
At Orbital Insight, we’ve built a platform that combines geospatial data with machine learning. It allows users to select any location worldwide and analyse activity over time using computer vision and geolocation algorithms. For example, one of our customers requested a train detection algorithm to provide novel economic activity monitoring capabilities across different countries. This allows a single user to monitor country-scale rail networks and be alerted to significant changes at any key locations.
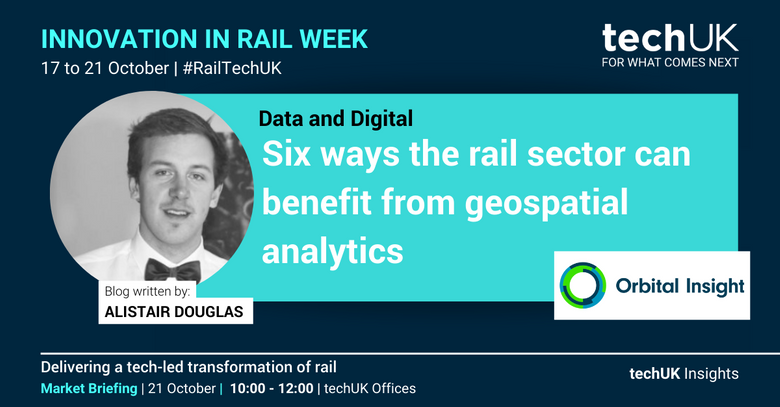
We generated our training data in-house using a global dataset of rail yard locations. Polygons were drawn around each train and our data set consisted of 30,000 trains across 141 distinct train yards
The image on the left shows our ground truth polygons at a rail yard in Brooklyn, Illinois. The image on the right shows our model’s detections at this rail yard. There were 150 true positives, 6 false positives, and 6 false negatives detected.
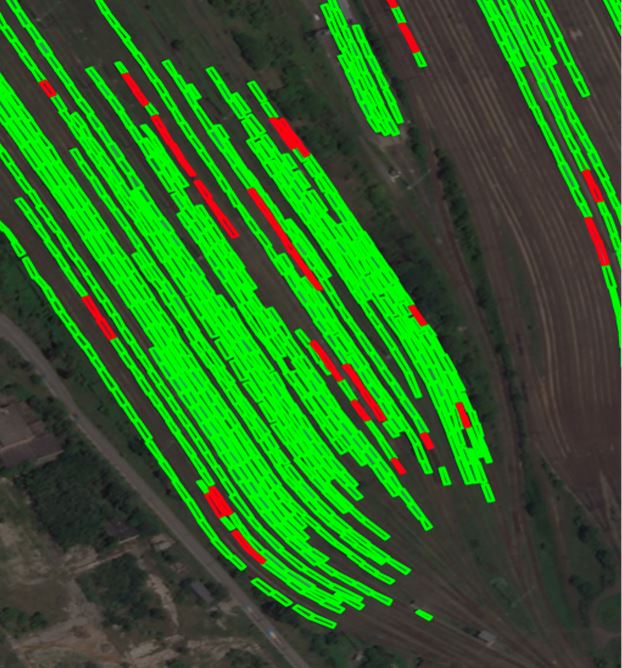

This image shows an annotated rail yard in Budapest, Hungary, with 848 trains. Trains are annotated in green, and flatcars are annotated in red.
For a deep dive into the technical details of this algorithm, check out our blog here: Applying Computer Vision to Railcar Detection.
Summary
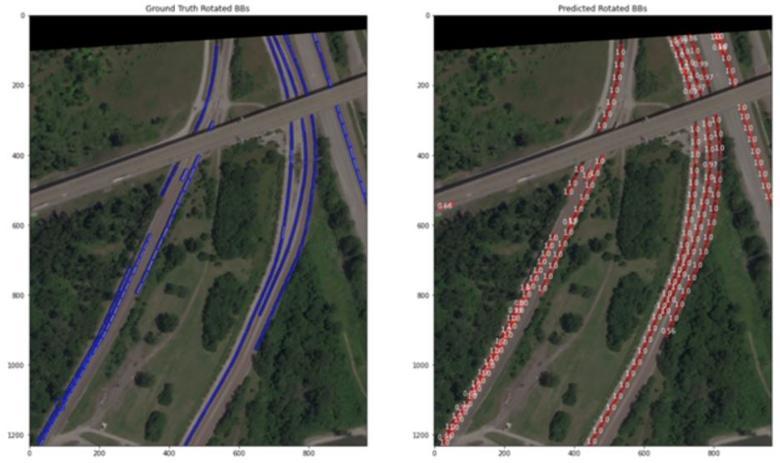
With access to counts at thousands of train yards across many countries, our customer now has near real-time monitoring and alerting to economic slowdowns, buildups of trains and supply chain disruptions for key freight across industries.
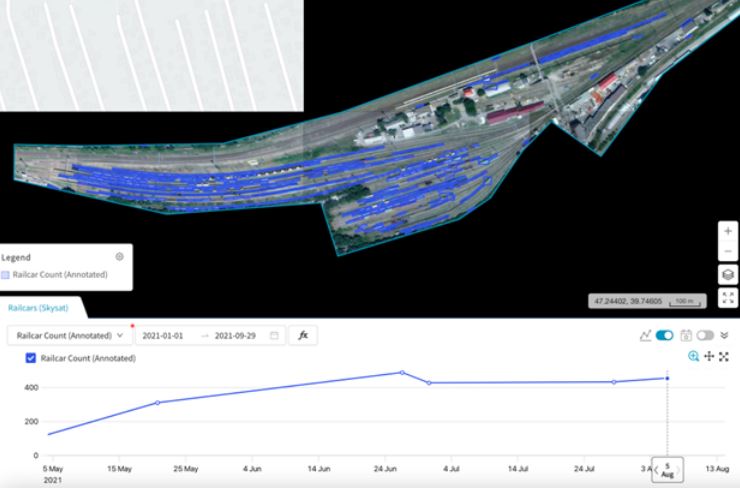
This image shows train detection counts over time. With regular satellite imagery tasking, the time series clearly shows any deviations from normal train counts.
To summarise, geospatial data can help companies supporting the UK rail industry in network analysis, train counting, route planning, demand planning, safety and marketing. At Orbital Insight, we’re building algorithms to extract insights from multiple geospatial data sources. We help decision-makers solve some of the toughest problems and provide a range of solutions using our easy-to-use platform; whether that’s train demand optimization, detecting unused rail cars or improving network safety.
Get involved with our work
All of techUK’s work is led by our members – keep in touch or get involved with our work on transport and infrastructure by joining our groups.




